Table of Contents
Internal Links vs External Links: What’s the Real Difference and Which Should You Use for SEO?
If you’re a web owner and a blogger you must have heard of the recent Google Update roll out on Internal and External links and how it may affect your site this 2026.
However let’s talk about Internal Links vs External Links and how to use it properly to afford ranking disorders.
SEO and website building, links are far more than simple pathways from one page to another. They’re the arteries of your site guiding search engines, shaping site structure, and influencing how far your content reaches.
But not all links are created equal. There are two major types of links every site owner should understand: internal links and external links (or backlinks).
Understanding how they differ and how to use each wisely can make the difference between a hidden blog and a website that ranks, converts, and grows.
What Are Internal Links?
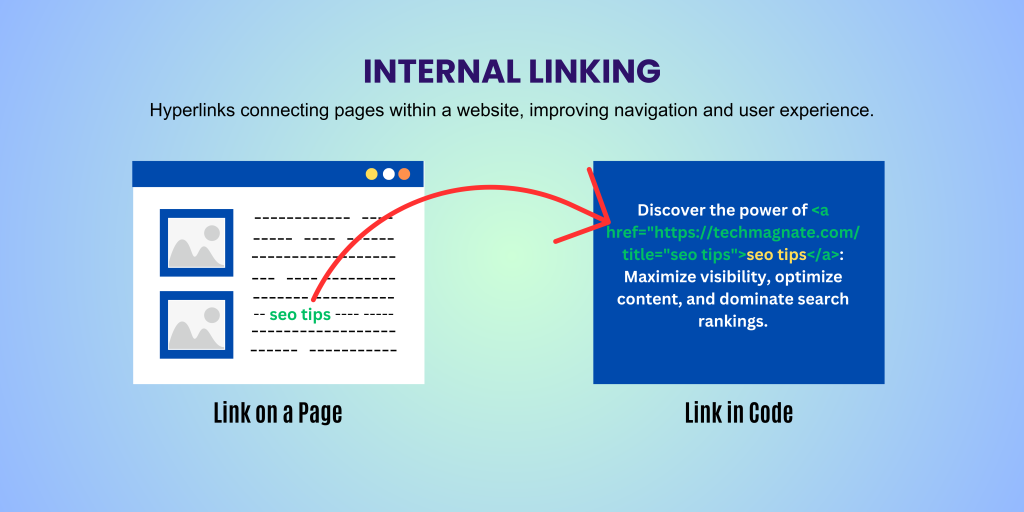
Internal links are links that point from one page on your website to another page on the same website.
For example, when your blog’s article about “How to optimize website speed” links to another article on your site titled “Best hosting providers in Nigeria,” that’s an internal link.
Types of Internal Links
- Contextual links — links embedded in your content (e.g. in body text).
- Navigation links — menu items, header navigation, footer links.
- Sidebar or widget links — related posts, recent posts, category links.
- Breadcrumb or internal indexing links — helps structure and guide readers (and crawlers).
Internal links are powerful because they help both users and search engines navigate your content, discover related pages, and understand how pages relate to each other.
What Are External Links (Backlinks)?
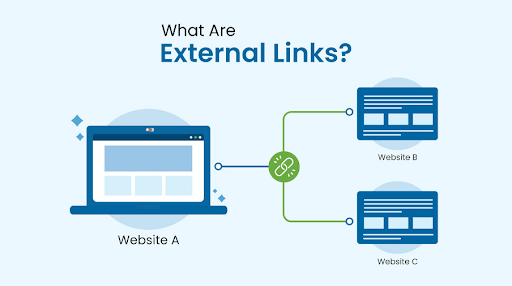
External links are links that point from your website to a different domain — or links from other websites that point to your domain. Often when SEO experts say “backlinks,” they mean external links coming to your site.
For instance:
- If you link from your blog to Wikipedia or a news website, that’s an external (outbound) link.
- If another blog links to your article — that’s a backlink, another form of external link.
External links are a core part of how the web works they help build context, trust, and authority, because they show readers (and search engines) that your content connects to a larger information network.
Internal vs External Links — Key Differences (at a Glance for better understanding )

| Feature | Internal Links | External Links / Backlinks |
|---|---|---|
| Destination | Same domain (around your site only) | Different domain (To or from another website) |
| Control | Full control (you add or remove) and links you don’t want anymore | Partial or no control — depends on other sites owners |
| SEO Impact on Your Site | Helps structure your site; spreads link value internally | Adds authority and trust when other reputable sites link to you or the other sites |
| Crawlability / Indexing | Improves easy crawling and indexing of all pages | Helps search engines evaluate trustworthiness and relevance |
| Risk/Ranking Errors | Low — depends on how you link internally | Higher — low-quality or spammy backlinks can harm SEO and probably Google delist |
| Use Case | Use for Site navigation, SEO structure, content organization | Use for SEO authority, traffic referral, credibility |
Why Internal Links Are Important and Needs not to be Underestimate
• Help Search Engines Crawl & Index More Pages
Search engine bots follow links to discover and index pages.
A strong internal linking structure ensures these bots can reach deep pages especially important for large sites or blogs with many posts.
• Spread “Link Equity” Across Key Pages
When a page has strong metrics (visits, backlinks, authority), internal links pass some of that strength to other pages.
This means your cornerstone content can help boost lesser-known articles.
• Improve User Experience & Engagement
Internal links guide readers to related content, keeping them longer on your site, decreasing bounce rate, and improving dwell time all positive signals for SEO.
• Help Organize Site Hierarchy & Thematic Structure
By linking related pages, you clarify topical clusters: what topics you cover, how they relate, and which pages are most important.
This helps search engines understand your site’s structure and expertise.
Why External Links (and Backlinks) Still Matter for 2026
• Build Authority and Trust
When credible, high-authority websites link to your content, it signals to search engines that your content is valuable, trustworthy, and relevant.
• Drive Referral Traffic & Broaden Reach
External links bring real human visitors from other sites — expanding your audience outside your own domain.
• Provide Context & Validation for Your Content
Citing reputable external sources (studies, references, authoritative sites) improves content credibility and gives value to your readers.
• Demonstrate Relevance to Search Engines
Outlinks to relevant, top-tier sources help search engines understand your content’s topic and context — making your own content more reliable and link-worthy.
Best Practices: How to Use Internal & External Links Wisely nowadays
Use Descriptive Anchor Text (Not “Click Here”)
Anchor text should describe what the target page is about: e.g. “Cloud VPS Hosting” rather than “click here.” It improves clarity for users and bots.
Link Related & Relevant Content
Only link to pages that truly add value or context. Irrelevant linking confuses users and dilutes SEO value.
Avoid Overloading Pages with Too Many Links
While internal links are helpful, too many can look spammy; same with external links. Balance them wisely.
Maintain Internal Link Structure — Update & Audit Regularly
As you add new posts or pages, remember to integrate them into your internal linking system. Also check for broken links or outdated references.
Vet External Links & Build Quality Backlinks
Link out only to trusted, authoritative sites. For backlinks: aim for high-quality, relevant sites — avoid link farms or spammy sites.
Prioritize Internal Linking First, Then Build Backlinks
A solid internal structure helps you get more value out of every backlink — because you control internal linking.
How a Great Host (Like HarmonWeb) Supports Your Links Strategy & SEO
While thoughtful linking is Good, your hosting infrastructure actually plays a “behind-the-scenes” role in how well search engines crawl and index your site:
- Fast server response times ⇒ crawlers can scan more pages quickly.
- High uptime & stability ⇒ bots aren’t met with errors or downtime.
- Clean, efficient HTML and server stack ⇒ aids proper parsing and indexing.
- Support for scalable traffic and content ⇒ you can build many pages without performance issues.
With a hosting provider that prioritizes performance and reliability like HarmonWeb your site is better positioned to benefit fully from both internal and external link strategies.
However , you need to put this in your mind that inLinks are more than connections between pages they are signals.
Internal links give structure, enhance crawlability, and guide users (and bots) through your site.
External links (backlinks and outbound links) build trust, authority, and referral traffic.
When you use both strategically with clear linking practices and strong hosting you set up a website that ranks better, loads faster, and delivers better value to readers.
READY TO HOST YOUR SITE OT TRANSFER TO HARMONWEB? LETS GET STARTED THEN




